Architectural Glass refers to glass that is specifically designed and utilized in the field of architecture and construction. It is a versatile material that serves both functional and aesthetic purposes in building design. Architectural glass is used in various applications, such as windows, doors, facades, partitions, skylights, and interior elements.
simplified types of glass commonly used in architecture:
Float Glass: Basic, flat glass used in many applications.
Tempered Glass: Stronger and safer glass that breaks into small pieces.
Laminated Glass: Glass layers bonded together with a safety interlayer.
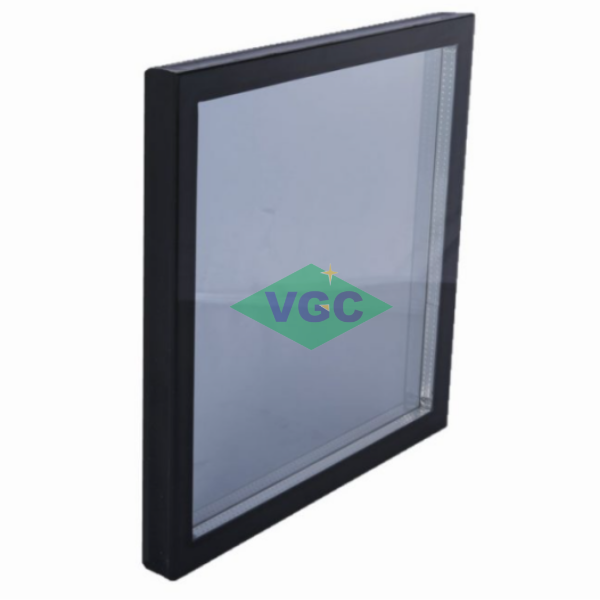
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs): Two or more glass panes with an air or gas-filled space.
Low-E Glass: Glass with a coating to control heat transfer.
Tinted Glass: Glass with added color to reduce glare and heat.
Frosted Glass: Glass with a textured or translucent surface for privacy and diffused light.
Patterned Glass: Glass with decorative patterns or textures.
These simplified descriptions give you an overview of the different types of glass commonly used in architectural applications.